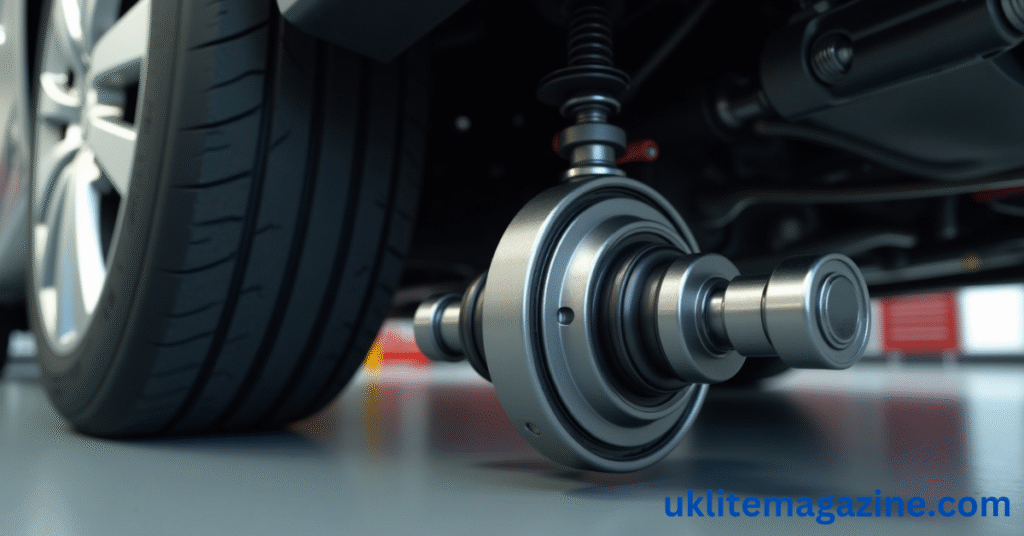
The constant velocity joint (commonly called CV joint) plays a critical role in your car’s drivetrain. It ensures smooth power delivery to the wheels, especially when turning or driving on uneven surfaces. Understanding how it works helps you recognize signs of wear and take timely action to prevent costly damage.
In this article, we’ll explain the complete mechanism of a CV joint, how it differs from other joints, and why it’s vital to your vehicle’s performance.
What Is a Constant Velocity Joint?
A constant velocity joint is a mechanical component used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles. It’s found at both ends of the CV axle — which connects the transmission to the wheels — and allows the wheels to receive power while accommodating the up-and-down motion of the suspension and the turning motion of the wheels.
Unlike traditional universal joints, CV joints can transmit power at a constant rotational speed, regardless of the angle.
Parts of a Constant Velocity Joint
A CV joint consists of several key parts:
-
Outer housing – encases the joint
-
Ball bearings – enable smooth rotation
-
Cage – holds the ball bearings in place
-
Inner race – fits into the axle shaft
All of these are packed with special grease and covered with a rubber boot to keep out dirt and moisture.
How a Constant Velocity Joint Works
The main job of the CV joint is to transmit torque from the engine to the wheels while compensating for steering angles and suspension movement.
Here’s how it works step by step:
-
Power Transmission
-
When the engine runs, it sends power to the transmission. From there, the CV axle transfers that power to the wheels.
-
Angle Compensation
-
As your car turns or the suspension moves up and down, the angle between the axle and the wheels changes. The CV joint adjusts its position while still spinning, maintaining a constant speed and smooth rotation.
-
Ball Bearings Movement
-
The ball bearings inside the CV joint slide within the grooves of the housing and inner race. This allows for both rotation and flexibility, even at sharp angles.
-
Boot Protection
-
A rubber boot surrounds the CV joint to hold grease inside and keep contaminants out. If this boot gets torn, grease leaks out, and dirt can enter — leading to CV joint failure.
Types of Constant Velocity Joints
There are two main types:
-
Ball-Type (Outer CV Joint):
Found near the wheel, it handles both rotation and wheel turning. -
Tripod-Type (Inner CV Joint):
Found near the transmission, it handles movement as the suspension moves up and down.
Why CV Joints Are Important
-
Smooth Driving: They allow power transfer without vibration.
-
Reliable Steering: They adjust to different wheel positions.
-
Efficient Performance: Less power is lost compared to older joint types.
Without CV joints, vehicles wouldn’t be able to make sharp turns or handle road bumps smoothly.
Signs of a Failing CV Joint
Recognizing early signs of failure can save your car from severe damage:
-
Clicking or popping noise when turning
-
Grease on the inside of wheels (from a torn boot)
-
Vibration while driving
-
Clunking noise during acceleration
If you notice any of these, get your CV joint inspected.
Conclusion
The constant velocity joint may be small, but it plays a big role in keeping your car’s drive smooth and reliable. By understanding how it works and recognizing early warning signs, you can extend its life and avoid expensive repairs.
Always check the CV boot during regular maintenance and replace worn joints promptly. A healthy CV joint ensures your car runs safely and efficiently on any road.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does a constant-velocity joint do?
A constant-velocity joint allows the transmission of power from the vehicle’s engine to the wheels while enabling the suspension to move and the wheels to turn, all without causing speed variation. It ensures a smooth and constant rotation, especially while steering or driving over uneven roads.
Can I drive if my CV joint is bad?
Driving with a bad CV joint is not recommended. While you might be able to drive short distances, a failing CV joint can break completely, causing loss of control or leaving your vehicle immobile. It’s best to repair or replace it as soon as symptoms appear.
What is the difference between a CV joint and a universal joint?
A CV joint maintains constant rotational speed at various angles, making it ideal for front-wheel-drive vehicles. A universal joint (U-joint), commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, can cause speed fluctuations when bent at sharp angles and is less efficient than a CV joint.
What is the function of the CV axle?
The CV axle connects the transmission to the wheels and transmits power for movement. It has CV joints at both ends, allowing for smooth rotation even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves. It’s essential for maintaining consistent power flow to the wheels.